Abstract
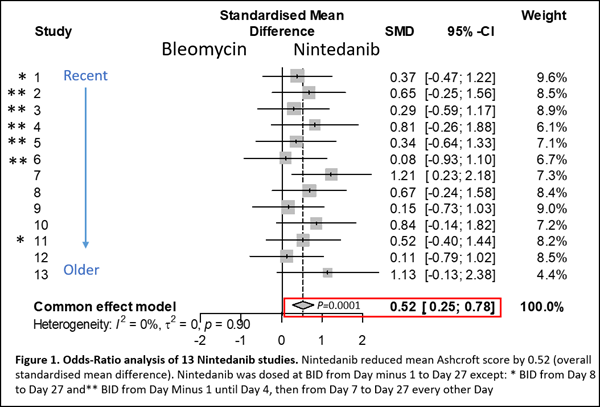
Background:IPF is a progressive and irreversible disease with high mortality. Nintedanib treatment reduces lung function decline but is not always well tolerated. Rat lung fibrosis induced by bleomycin instillation mimics aspects of human IPF and this animal model is used to assess efficacy of novel IPF therapies. Here we compared Nintedanib use in 13 rat bleomycin studies to examine efficacy trends and to estimate pooled effect sizes. Method: Male SD rats challenged with bleomycin by the oropharyngeal route and received vehicle or Nintedanib twice daily at 60 mg/kg until Day 28. Lung sections stained with Picrosirius Red were scored blindly by a Pathologist for fibrosis. Ashcroft means and medians from 13 studies were pooled (120 bleomycin/vehicle and 117 bleomycin/Nintedanib rats). Nintedanib?s mean effect size was estimated using odds-ratio analysis. Median Ashcroft scores were also compared across studies. Result:Mean and Median Ashcroft score was 2.37 and 3 in controls. Nintedanib reduced standardised mean Ashcroft score by 0.52 [95% CI 0.25 to 0.78]. In combined studies Nintedanib reduced median Ashcroft score by 1 (P<0.001)(Figure 1). Within individual studies pairwise comparisons were unlikely to yield low P-values. Conclusion: Nintedanib consistently shows a minimal to mild antifibrotic effect in our rat lung fibrosis model supporting the use of Nintedanib as a reference compound.