Abstract
Aim: To assess ventilatory management of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure against National Adult NIV Audit standards, identify gaps in provision, and develop educational material to optimize provision as per BTS Guidlines
Methodology:Retrospective analysis of 37 patients at a DGH over 10months initiated on NIV for acute hypercapnia within 24 hours of admission, with data collected on NIV initiation and setting adjustments.
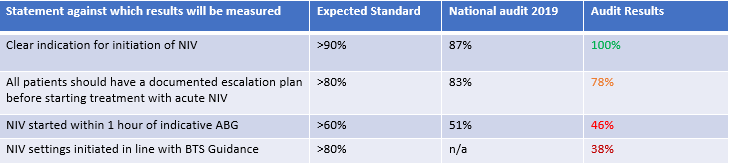
Results:Only 1 parameter met the standards-clear indications of initiating NIV were documented in 100% of cases, against the standard of 90%. Of the rest, an escalation plan being put in place was closest to meeting the standard, with 78% against a standard of 80%. DNACPR being in place measured at 60% against a standard of 70%. 46% had NIV initiated within 1 hour of an indicative ABG versus a standard of 60%. 38% of patients had their NIV settings initiated as per BTS guidelines against a standard of 80%. Post Initiation ABG,95% of patients did not show an improvement in their pCO2 value, indicating sub-therapeutic delivery of NIV. Mortality was calculated at 24%.
Conclusion:NIV provision overall falls short of the national standard. We recommend an NIV prescription form be enacted that would provide key information on timing of initiation, initial settings and how to change them. We propose a series of theoretical and practical teaching sessions, targeted at all colleagues who may interact with NIV patients.