Abstract
Purpose
To investigate whether alveolar collapse detected by an extension of Parametric Response Maps (PRM) can be used as a predictive marker in IPF.
Methods
A CT scan was performed in inspiration and expiration on 66 IPF patients. PRMs were created as scatterplots of the voxel-wise attenuation values of the paired inspiration and expiration scans. The PRMs were used to calculate lung parenchymal subvolumes as a function of their attenuation changes during inspiration and expiration. Volumes of ?collapsed? lung tissue on expiration were calculated as a percentage of Normal Attenuation Areas (NAA) and High Attenuation Areas (HAA) per patient (NAAcollapse/NAA; HAAcollapse/HAA, respectively). After each respective 3-year period of observation, patients were divided into two subgroups based on their status (endpoints: death and transplantation or still under clinical observation). To compare the named CT parameters obtained at baseline, a Mann-Whitney U test was used.
Results
At the end of the 3-year individual follow-up, 37 patients were still under clinical surveillance, whereas 29 patients had died or undergone transplantation. NAAcollapse/NAA and HAAcollapse/HAA differed significantly between subgroups (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively).
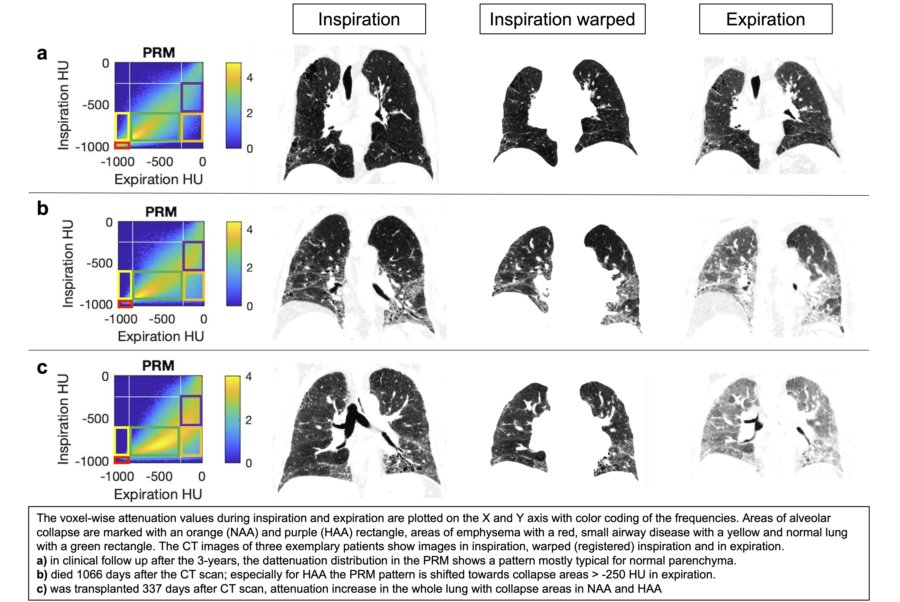
Conclusion
The PRM technique can be used to demonstrate the concept of alveolar collapse as a prognostic marker in IPF patients.