Abstract
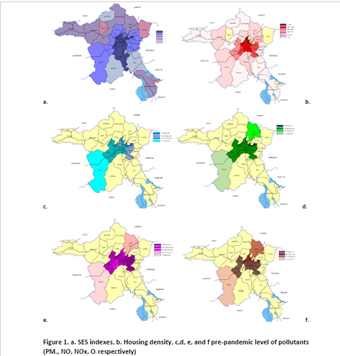
We aimed to show the relation between COVID-19 mortality and socioeconomic status (SES),air pollution,and housing density in the districts of Ankara.Mortality data were collected from three cemeteries where burials were held between 10.03.2020-31.05.2022 due to COVID-19.Housing density was calculated by dividing the number of households by the area of the district in square kilometers.SES index of districts is numerical data stratified into 5 categories.Air pollution data for the last 5 years prior to the COVID-19 pandemic was obtained from the North Anatolia Clean Air Regional Directorate (See Fig.1).Table1 shows correlation of COVID-19 mortality rates with variables.Average household size(r=0.50, p=0.02) and O3 levels(r=0.77, p=0.02) were correlated with elderly deaths due to COVID-19.There was a statistically significant relationship between NO(r=0.64, p=0.03),NOX (r=0.84, p=0.004), O3(r=0.82, p=0.01),and housing density(r=0.64, p=0.001) in elderly males and NO(r=0.76, p=0.02), PM2.5(r=0.76, p=0.03), housing density(r=0.48, p=0.02) in elderly females COVID-19 mortality rates.Our study has the distinction of being the first one demonstrating this relationship for Ankara.
Table1.Correlation of COVID-19mortality rates with variables
| N | % | r | p | |
| NO | 5975 | 93 | 0.80 | 0.01 |
| NOX | 5975 | 93 | 0.78 | 0.01 |
| PM2.5 | 5888 | 92 | 0.74 | 0.01 |
| O3 | 3913 | 61 | 0.84 | 0.01 |
| SES index | 6384 | 100 | 0.48 | 0.03 |
| Housing Density | 6384 | 100 | 0.68 | 0.001 |