Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
The aim of this study is to evaluate and compare the respiratory sequelae and quality of life in patients admitted to the ICU with severe Covid-19 according to their previous vaccination status.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
Observational, case-control, retrospective study of patients admitted to ICU with Covid-19. From December 2020 to January 2022, 51 previously vaccinated patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection were identified and matched (according to age, sex and period of ICU admission) with 51 unvaccinated patients. Respiratory sequelae (lung function test and exercise capacity) and quality of life (SF-12) were evaluated at 6-months after hospital discharge.
RESULTS:
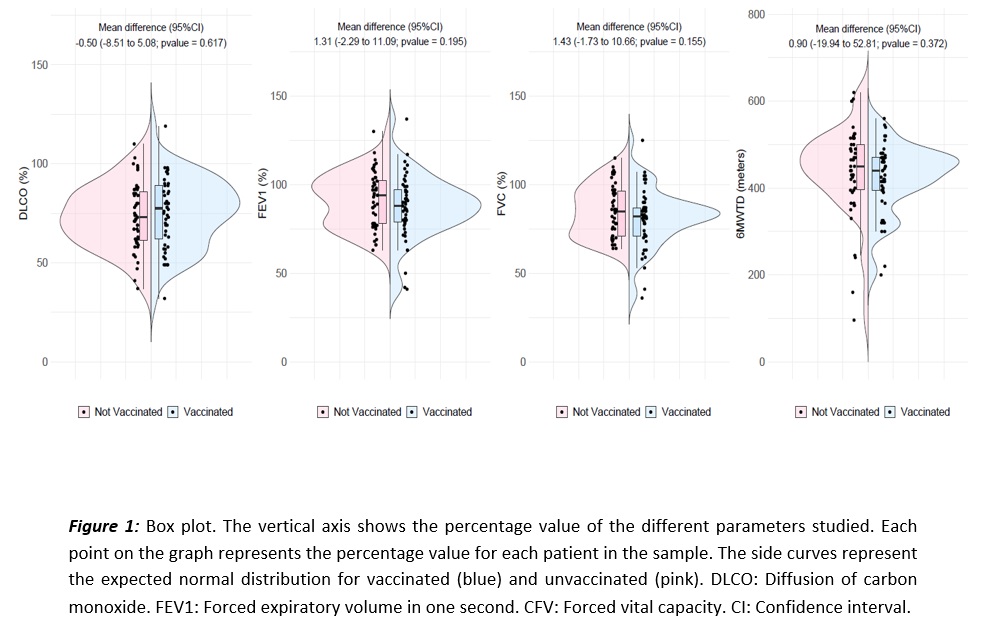
No differences were found between baseline characteristics and disease severity at ICU admission. No significant differences were observed in spirometric values, mean percentage of predicted lung diffusion capacity (73.5% vs. 75.2%; p=0.62), mean distance walked in the 6-minute walking test (441 vs. 424 meters; p=0.37) and quality of life (physical domain: 46 vs. 48; p=0.64 and mental domain: 52.7 vs. 50.7; p=0.57) between non-vaccinated and vaccinated patients (Figure 1).
CONCLUSIONS:
No differences were observed in terms of respiratory sequelae or quality of life in critically ill COVID-19 patients 6-months after hospital discharge based on previous vaccination status.
Supported by: CIBERES-UCI-COVID (ISCIII COV20/00110)