Abstract
Pleural infection is common and it is associated with poor outcomes like mortality and long term hospitalization. RAPID score is used to predict these outcomes, by evaluating renal function, age, fluid purulence, infection source and serum albumin. It is divided in 3 categories: low (0-2 points), medium(3-4 points) and high(5-7 points)risk.
The purpose was to verify the correlation between mortality and hospitalization length and the calculated score.
The authors evaluated 51 patients with empyema in a retrospective study between June/2014 and February/2023. Hospitalization length and mortality were stratified by RAPID score categories and SPSS was used for statistical analysis.
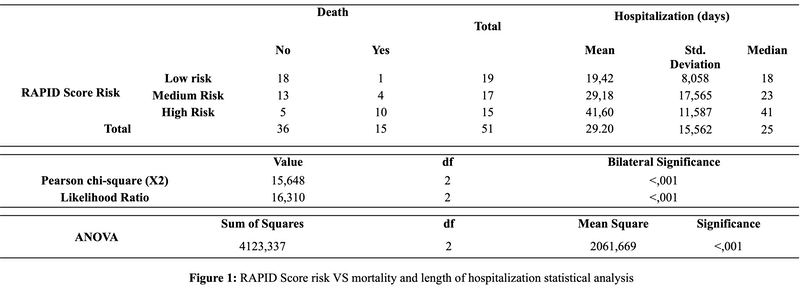
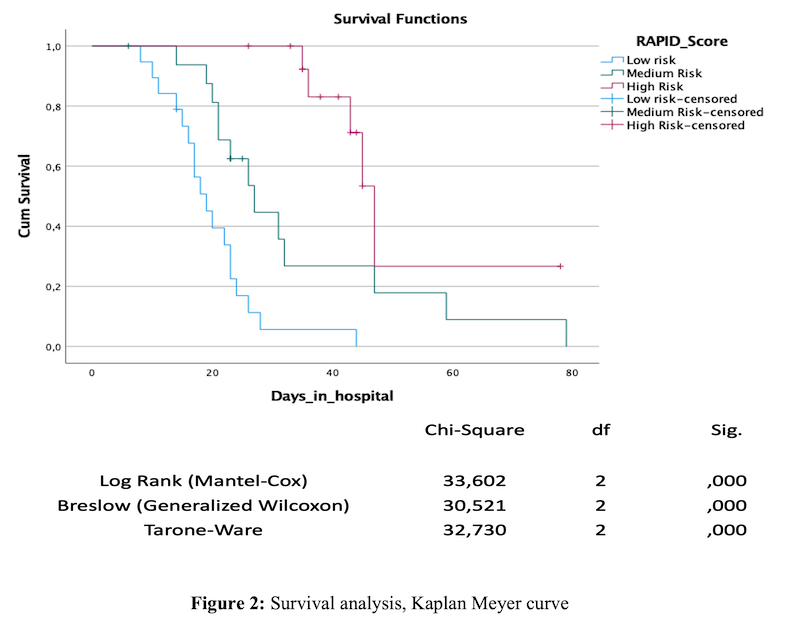
There was an association between the low, medium and high RAPID score categories and mortality (5.3%, 23,5% and 66,7%, respectively)(X2:16; p<0.05) and hospitalization length (median 18, 23 and 41 days, respectively)(ANOVA 4123; p<0.05) (Figure 1). Median survival was 19, 27 and 47 days, respectively (Log RanK 33,602; p<0.05). (Figure2)
RAPID score is a useful tool to predict poor outcomes in patients with empyema. Further studies are needed to improve the treatment using this score.