Abstract
Background: Despite the association of lung protective strategy with improved survival in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the implementation remains low.
Aims and objectives: To assess the potential of utilizing business intelligence (BI) for real-time data integration and visualization to enhance lung protective strategy.
Methods: The retrospective study conducted on patients with ARDS in 2 intensive care units (ICUs) between June 2020 and December 2022. Both ICUs implemented education for healthcare providers and introduced protocolized care. BI was introduced in one of the ICUs in September 2020, while the other ICU followed suit in July 2021. The main objective was to assess the implementation of low tidal volume (TV) ventilation of predicted body weight within 24 hours of ARDS onset.
Results: During the 31-month period, 486 patients were admitted to the ICUs with the diagnosis of ARDS. In the intervention phase, the BI-assisted group showed improvement in the compliance to low TV ventilation compared to the SOC group (79.1% vs 61.3%, p = 0.018). During the 18-month maintenance phase, consistent adherence to the low TV ventilation was maintained at 75.6% (Fig 1).
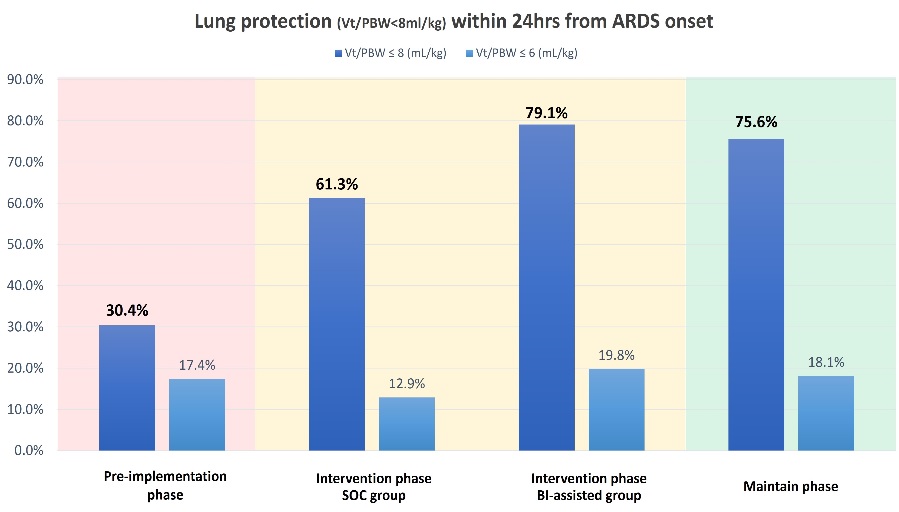
Conclusions: The use of BI to support data-driven decisions was found to improve compliance with low TV ventilation, and it was easy to maintain in the ICU.