Abstract
Rationale: Smoking patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) are at greater risk of developing pneumonia. How smoking behavior changes affect the risk of pneumonia hospitalization, however, remains unclear.
Methods: From 2009 and to 2018, we investigated the association between smoking change and the risk of pneumonia hospitalization in patients with DM. A total of 332,798 adult patients with DM from the Korean National Health Insurance System database who underwent health screening examination between 2009 and 2011, and smokers at the first health examination were included.
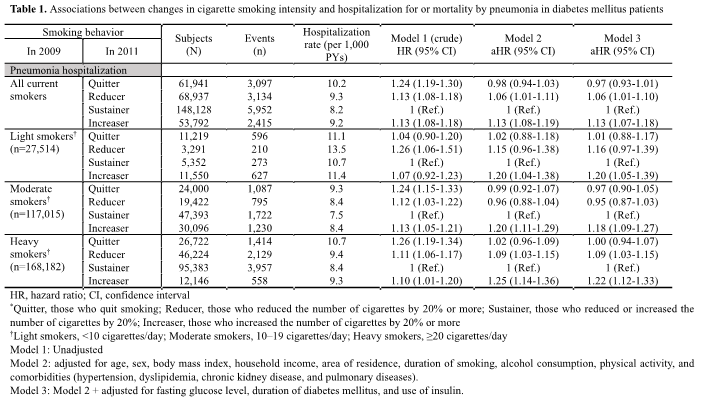
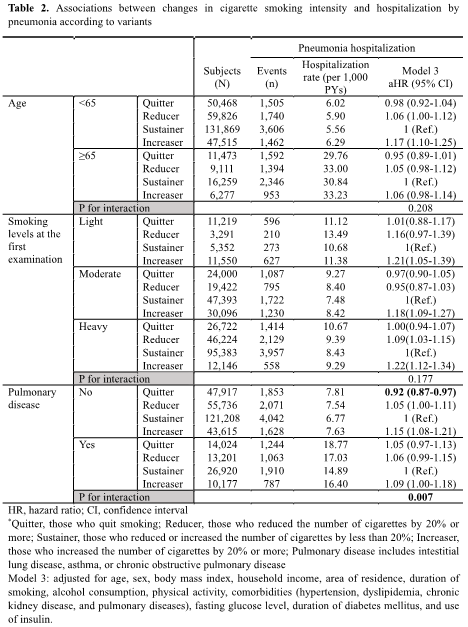
Results: During a mean follow-up of 4.89 years, 14,598 (4.39%) pneumonia hospitalization were identified. Reducers had a slightly increased risk of pneumonia hospitalization compared to sustainers, while quitters did not have a significant association. However, increasers had 13% higher risk of pneumonia hospitalization.
Conclusions: Our study showed that an increase in smoking intensity was associated with an increased risk of pneumonia hospitalization in people with DM. However, a protective effect of smoking reduction or cessation on pneumonia risk was not demonstrated.