Abstract
Aim: To establish if ABPT reduces the rate of air leak in patients with SSP and a persistent air leak (PAL) ?5 days.
Method: Prospective multicenter study conducted in three years. Rate of air leak was measured using a digital chest drainage device (Thopaz) for 48 hours before and 24 hours after ABPT (1.5ml/kg) via the chest drain.
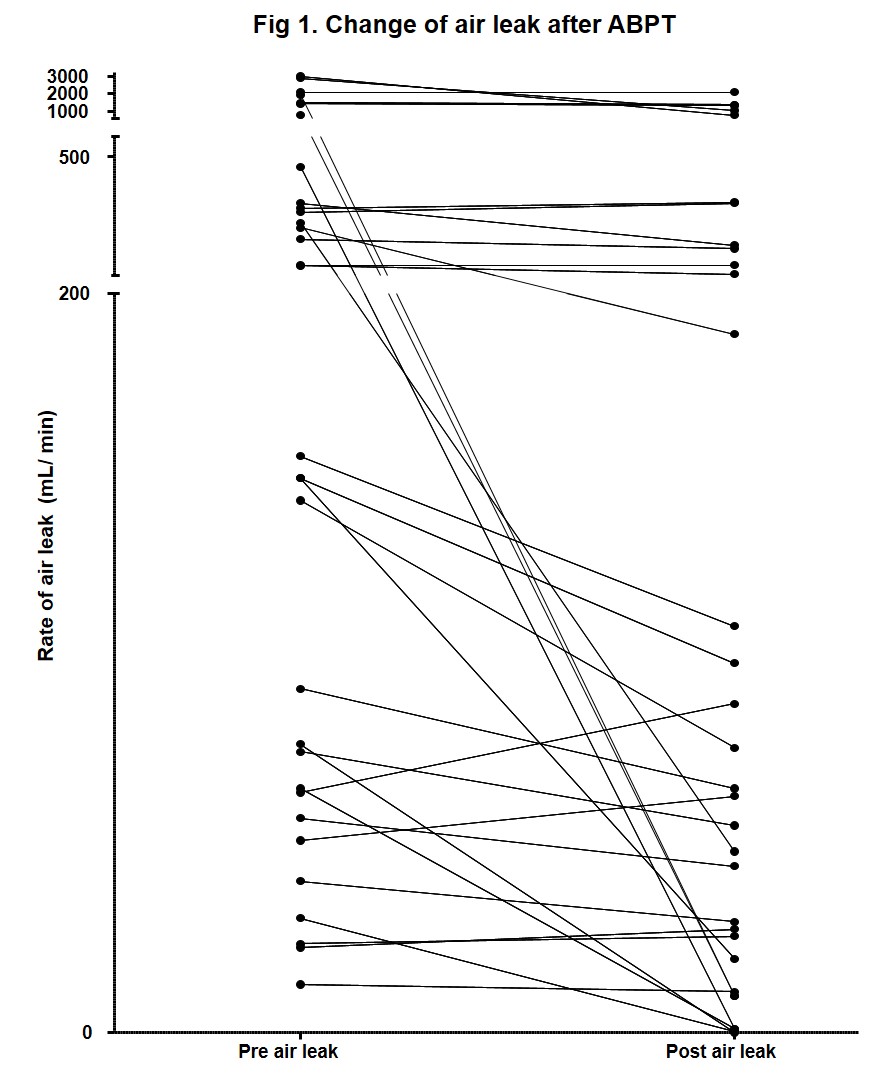
Results: 32 patients (31 male; mean age 71.4; 88% had COPD) had SSP and PAL (mean = 13.8 days of air leak before ABPT) received ABPT (29 had 1 dose; 3 given 2 doses). The rate of air leak reduced significantly from 192.5 [IQR 65-453] to 71.5 [21.5-278] ml/min 24 hours after one dose of ABPT, p<0.0001 (Signed Rank Test). Ten (30.3%) patients achieved >50% reduction in air leak. Eight (24.2%) achieved >80% reduction in air leak and had successful chest tube removal within 48 hours. No significant side effect (eg infection) was noted. No patient received surgery due to high surgical risk.
Conclusion: Intrapleural ABPT significantly reduces air leak in SSP patient with PAL and is safe. Confirmation with a randomized trial is needed.
Table 1 Results
| % patient with fully expanded lung | 56.3 |
| Average volume of autologous blood (ml) | 75.6 |
| % patient achieved ? 80% reduction in air leak after 2 dose of ABPT | 66.6 |
|
Adverse event including chest drain blockage, fever or pleural infection |
0 |
| Average length of hospital stay ( days) | 32.5 |
| No. Pneumothorax within 3 months | 3 |