Abstract
Background
Increased serum levels of the alarmin cytokine Interleukin (IL)-33 are associated with poor outcomes in hospitalised COVID-19 patients. Tozorakimab is an IL-33 neutralising monoclonal antibody.
Aim
To evaluate efficacy and safety of tozorakimab in the Phase 2a ACCORD-2 COVID-19 study (EudraCT:2020-001736-95).
Methods
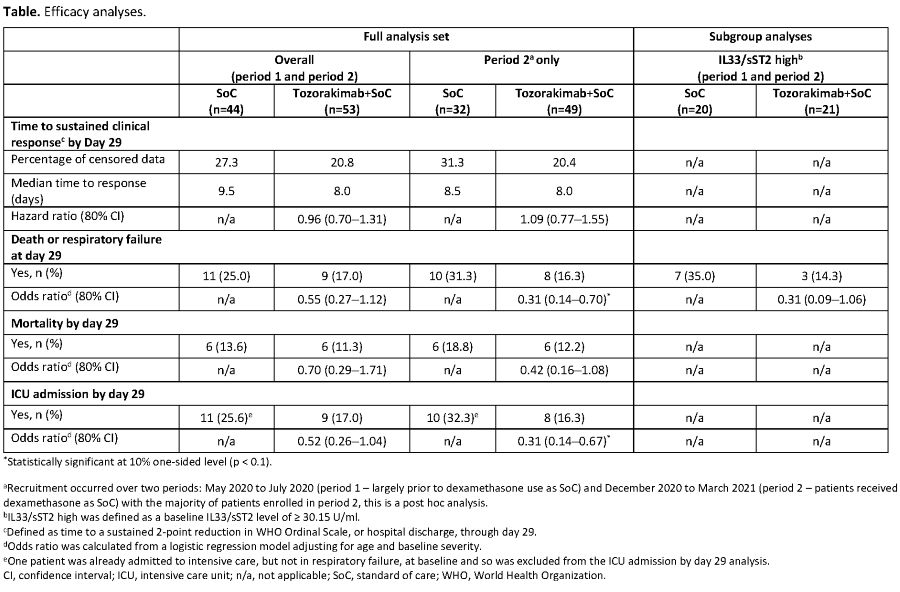
ACCORD-2 was an open-label, phase 2 adaptive study in adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (WHO Ordinal Scale score of 3?5), randomised 1:1 to tozorakimab 300mg+standard of care [SoC] or SoC alone. Recruitment occurred in two time periods; in period 2, dexamethasone was the SoC.
Primary endpoint was time to sustained 2-point clinical improvement or hospital discharge, with other endpoints including death or respiratory failure, mortality, ICU admissions and safety.
Results
Of 97 patients eligible for efficacy analyses, 53 received tozorakimab+SoC and 44 received SoC alone. Whilst median time to response was similar in both arms, tozorakimab numerically reduced the risk of death or respiratory failure, mortality, and ICU admissions vs SoC (Table), and was well-tolerated. Subgroup analyses suggest that high baseline serum levels of IL-33/sST2 complex may be a predictor of tozorakimab response (Table).
Conclusion
ACCORD-2 analyses suggest that tozorakimab may be a novel therapy improving outcomes in patients hospitalised with COVID-19.