Abstract
Background and aim: For the assessment of lung function decline that leads to air-flow limitation, we want to know the reference ranges as well as the point representative values of change rates.
Method: For subjects who underwent more than 5 tests in the study period, %FEV1 change rate(?%FEV1) is calculated from the linear regression between age and %FEV1. From mean(?), standard deviation(?, SD) of ?%FEV1 of healthy non-smokers (HNS), the lower limit of normal (LLN) or the lower 5th percentile is calculated. Expected FEV1 change rates (?FEV1) and their LLN that corespond to sex, age and height are calculated from ?%FEV1. The LMS method reference equations of Japanese Respiratory Society 20131) is used.
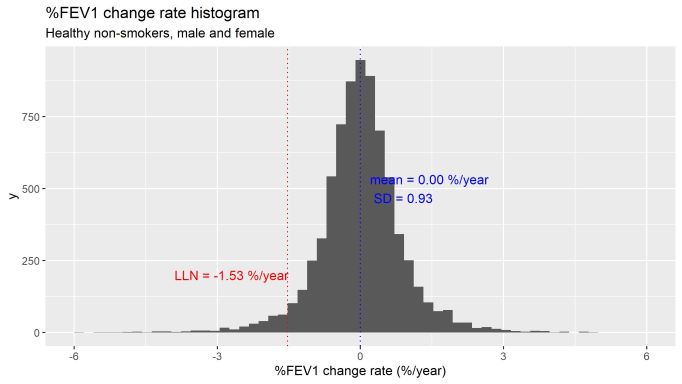
Results: 1955 male, and 5546 female HNS underwent for average 9.7 tests per subject between 2005 and 2019. The mean ?%FEV1 of HNS is 0.00%/y, SD is 0.92%/y, and LLN is -1.53%/y. ?FEV1 of average subjects are, for male (60 y.o, 169cm height), mean -22.8ml/y, LLN -69.8ml/y, for female (60 y.o, 156cm ), mean-11.5 ml/y, LLN -45.2 ml/y.
Conclusion: The LLN as well as the mean of ?%FEV1, ?FEV1 are calculated from the lung function dataset of a large number of normal subjects, which can help us interprete the spirometries of aging population and those at the risk of obstructive lung diseases.
1) Kubota M, et.al. Respiratory Investigation. 2014;52(4 ):242-250