Abstract
Background: Patients with comorbidities are at increased risk of pneumococcal disease and are often recommended for pneumococcal vaccination. In Greece, since 2015 the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) is recommended sequentially with the 23-valent vaccine (PPV23) for adults aged ?65 years and younger adults with comorbidities or other risk factors.
Aims and objectives: The EGNATIA study aims to assess pneumococcal serotype distribution in adults hospitalized with CAP.
Methods: This is a prospective study of adults aged ?19 years hospitalized with radiographically-confirmed clinical CAP in the regions of Ioannina and Kavala, Greece. Pneumococcus was identified using serotype-specific urinary antigen detection assays (UAD 1/2), BinaxNow® and conventional cultures. UAD1 detects serotypes in PCV13; UAD2 detects additional PCV20 & PPV23 serotypes.
Results: 1113 hospitalized CAP patients were enrolled during November 2017-October 2020. Mean age was 70.1 years. The most frequent comorbidities were diabetes mellitus (21.9%), coronary artery disease (15.7%) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, 14.5%). Pneumococcus was identified in 116 patients (10.4%). Pneumococcal serotypes are presented by PCV formulation and comorbidities (Table 1).
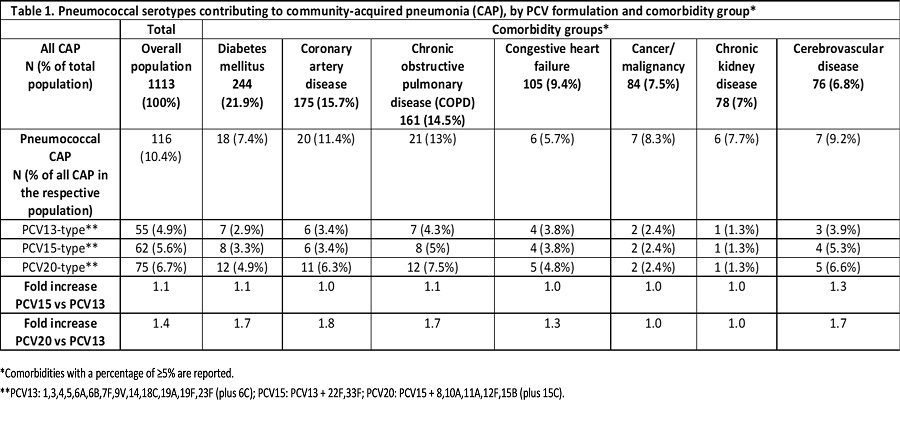
Conclusions: Expanded valency PCVs will increase coverage of pneumococcal CAP, particularly in patients with common comorbidities.