Abstract
Introduction
IE can be detected by visual review of NIV monitoring recordings. There are no validated non-invasive methods for its automatic detection.
Objectives
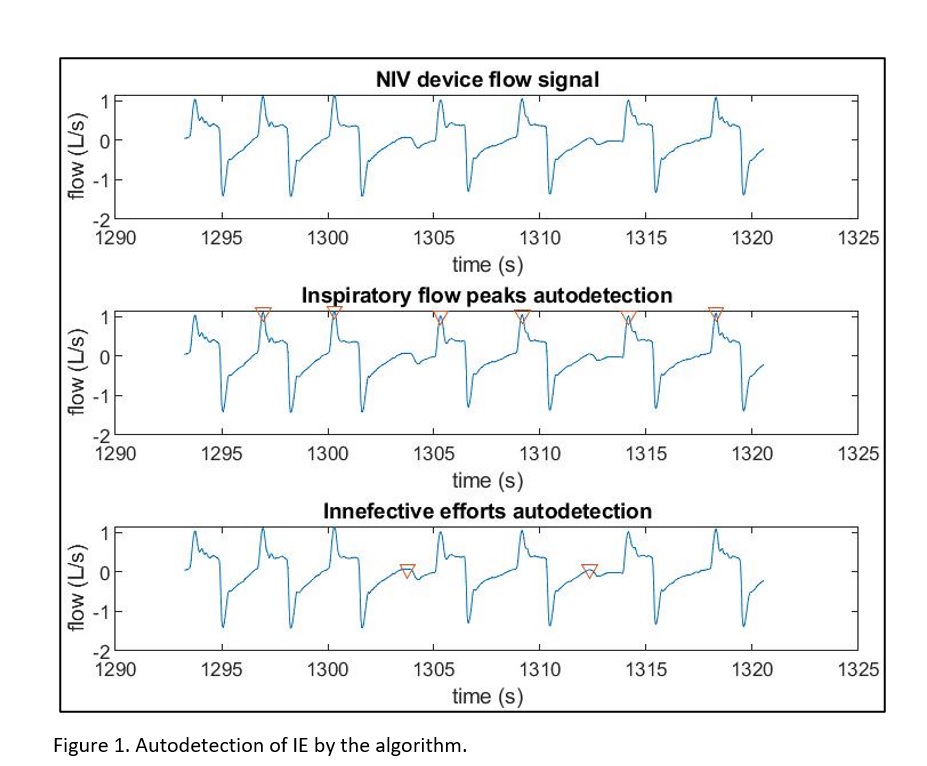
To validate an algorithm designed to detect IE through mathematical analysis of flow-time signal of NIV devices (Figure 1).
Methods
From monitoring records of stable patients under NIV, a set of different tracings with and without IE were selected. 4 NIV experts reviewed them and selected IE (agreement analysed by Kappa Index). Experts and algorithm diagnosis were compared by Kappa index and COR curve.
Results
22 patients were included (59,1 % women). Mean age was 63,5 years (SD 19,7). 45,45 % (10) had COPD; 27,27% (6) OHS; 22,72% (5) neuromuscular disease and 4,5% (1) congenital scoliosis. 21 NIV monitoring parts and 268 respiratory cycles were analysed.
Kappa index was above 0.8 (0.813-0.887) and statistically significant (p<0.001) in every comparison between all experts.
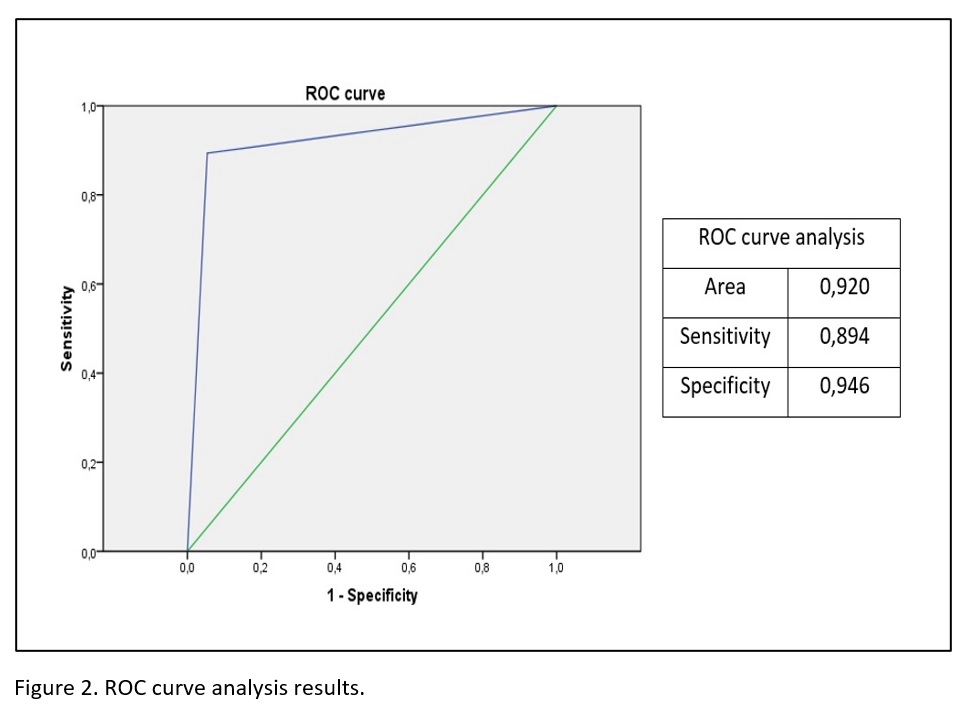
Agreement between the algorithm and experts was 0.801 (Kappa index, p<0,001). Its diagnosis accuracy is shown in Figure 2.
Conclusions
The algorithm showed a strong diagnosis accuracy and correlation with experts? diagnosis.