Abstract
Introduction:LCI measures ventilation inhomogeneity with potential to monitor children with a range of lung disease. Datasets from different commercial devices or washout gases cannot be assumed as interchangeable. Data has shown stability of LCI from childhood to adulthood. This study demonstrates normative data from children using one commercial device (ndd EasyOne Pro LAB) with nitrogen multiple breath washout (MBW)
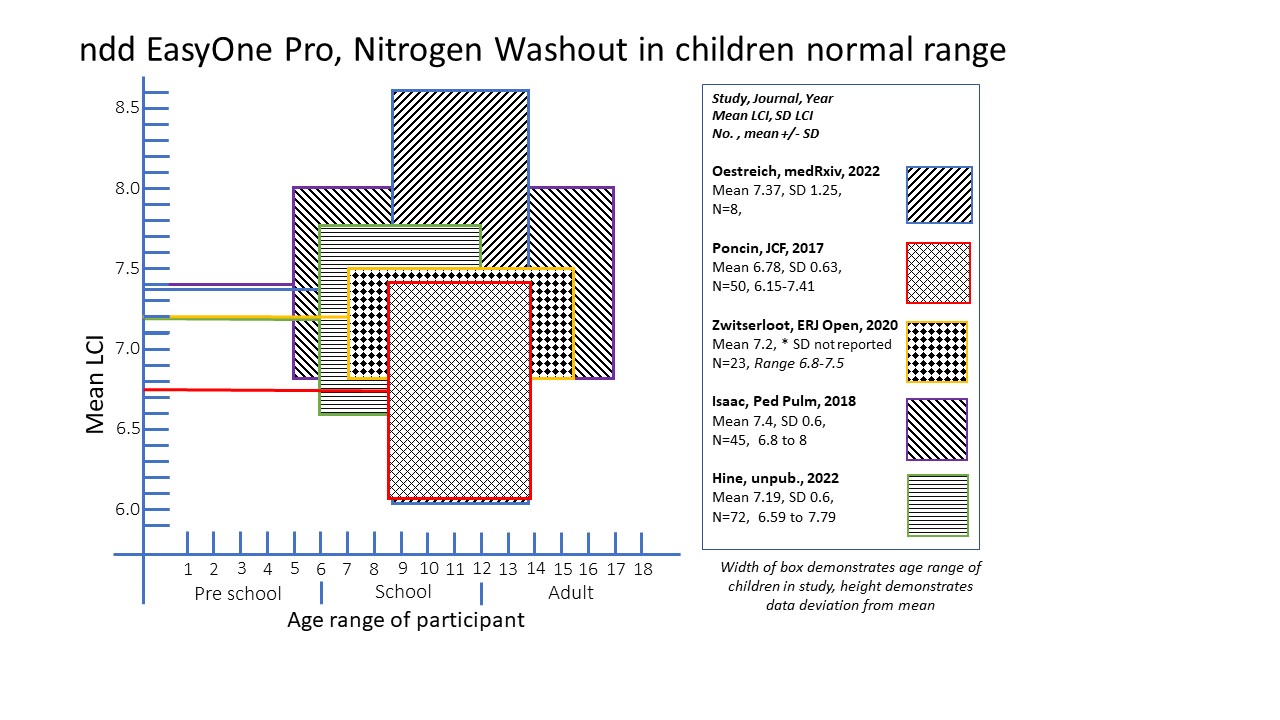
Method:A literature search was completed identifying 45 articles reporting results from the device with MBW. Data from healthy children (up to 18 years) was recorded, duplicate datasets removed. 4 studies in children were compiled. We performed LCI using the same device in healthy children aged 6-12 years using recommended MBW procedure
Results:72 children performed LCI, mean 7.19 (0.6 SD). This was in keeping with data from similar age groups; mean LCI range 6.78-7.4. Excluding one study with small subject numbers (8), the variation of LCI was similar (SD 0.6-0.63), a potential range of upper limit of normal would exist (8.0-8.5, mean+1.96*SD)
Conclusion:To be of value, robust, device and gas specific normative data must be available for the age of intended use. This is challenging given the variety of devices and limited number of specialist centres in which LCI is used with additional variation in acquisition techniques, software and quality control