Abstract
Introduction & aim Endobronchial valve (EBV) treatment has been shown to be beneficial for patients with severe emphysema. The FEV1 was found to be significantly higher compared to baseline up to 3 years after treatment although the magnitude of improvement gradually decreases over time. So far, it has not been investigated whether this treatment decelerates the decline in lung function. Therefore, our aim was to investigate the lung function decline before and after EBV treatment.
Methods We included patients who were treated with EBVs in our hospital, of whom pre-treatment spirometry results were available (at least 4 measurements within at least 2 years before treatment) and whom had an annual FEV1 measurement up to 3 years after treatment.
Results In total 45 patients were included (73%female, FEV1:28±7%, residual volume: 232±32%) who had a mean pre-treatment FEV1 decline of -60mL/year. Mean FEV1 ?decline? after treatment was +1ml/year, since FEV1 was still above baseline level at 3 years follow-up. However, the FEV1 decline between 1 to 3 year of follow-up was not significantly different compared to the pre-treatment decline (-73mL/year, p=0.357) (Figure 1).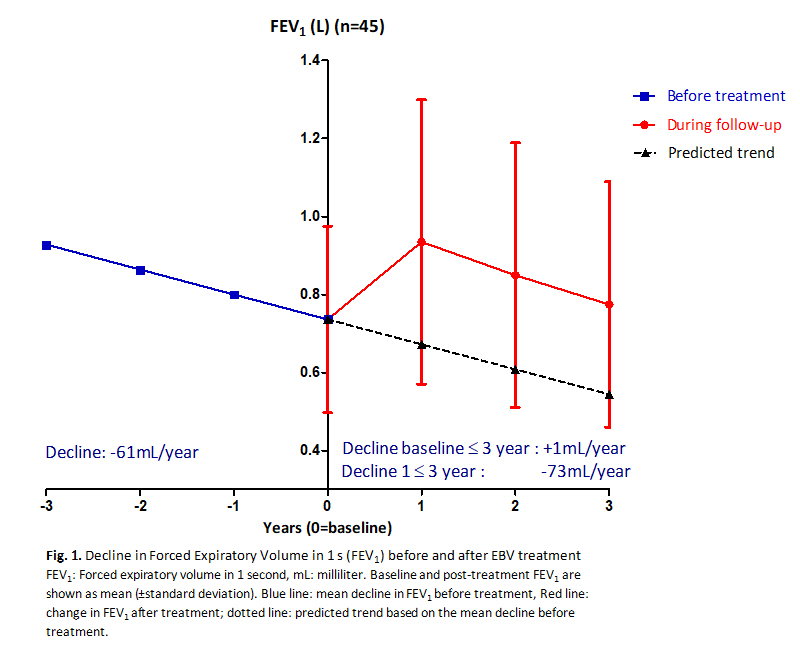
Conclusion Our results show that the EBV treatment does not influence the progression of disease in terms of lung function decline. However, the treatment does improve the FEV1 up to a level that is still comparable 3 years after treatment with baseline level.