Abstract
Objective: To determine the relationship between physical activity and handgrip strength in patients with nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD).
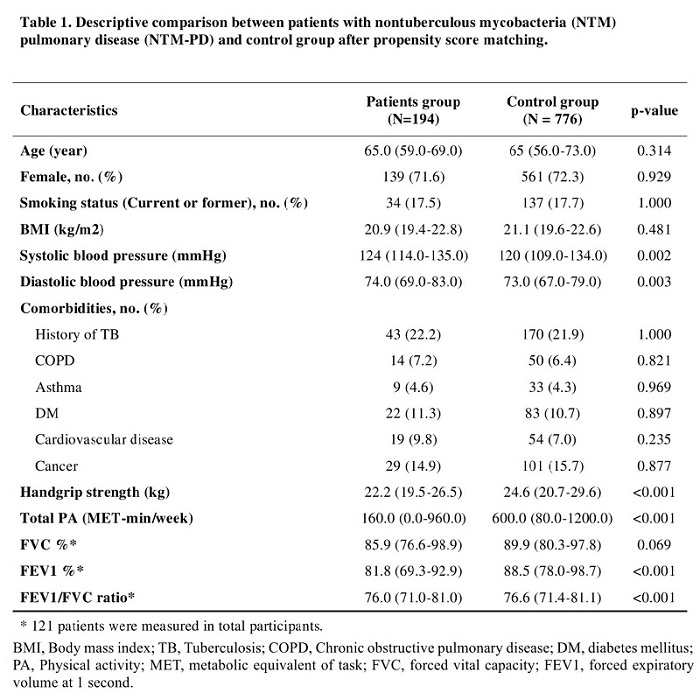
Methods: We conducted a propensity score (PS) matched case-control study of 194 patients with NTM-PD and 776 controls. Patients with NTM-PD were prospectively enrolled at the tertiary hospital between January 2022 and October 2022. The control group was selected randomly from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey from 2014 to 2019. PS matching was done using age, sex, smoking, body mass index, and comorbidity in a 1:4 ratio.
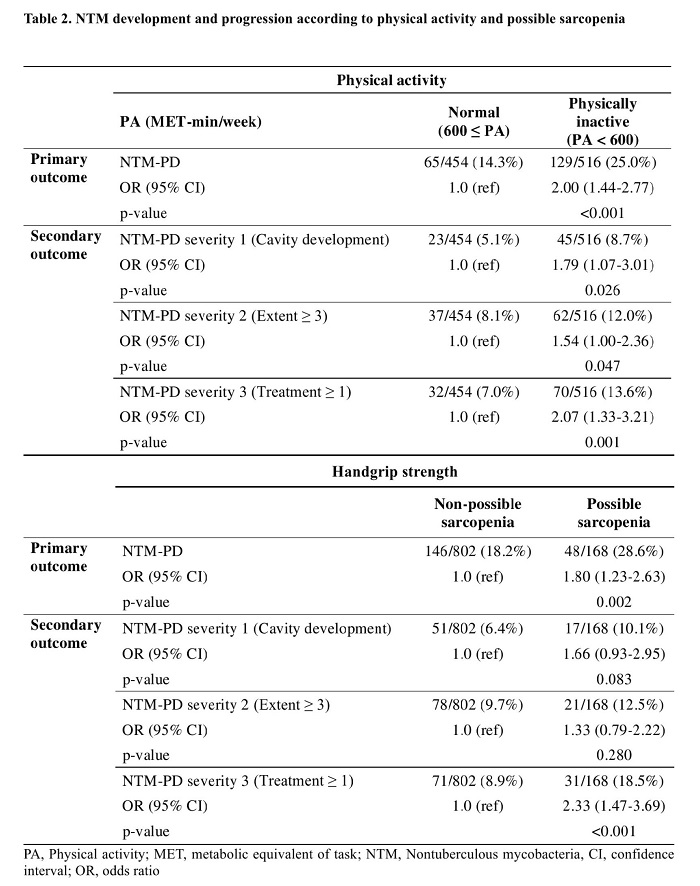
Results: Physical inactivity was significantly associated with NTM-PD (Odds ratio (OR), 2.00; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.44 to 2.77) and the severity of NTM-PD (OR 1.79; 95% CI 1.07 to 3.01; cavity development). Possible sarcopenia also had an association with NTM-PD (OR 1.80; 95% CI 1.23 to 2.63) but not with the severity of NTM-PD (OR 1.66; 95% CI 0.93 to 2.95; cavity development).
Conclusions: Physical inactivity was associated with NTM development and progression, and possible sarcopenia was related to NTM development.