Abstract
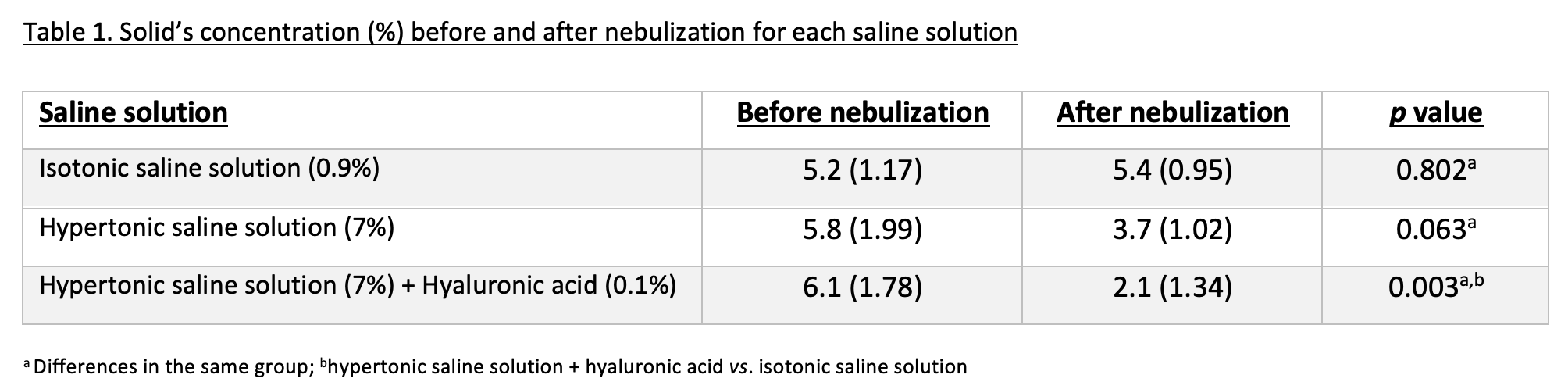
The aim of this study was to compare the changes in the solid?s concentration before and after nebulization of hypertonic saline (HS) vs. HS + hyaluronic acid (HA) vs. isotonic saline (IS) in bronchiectasis patients. Methods: This was a post hoc analysis (NCT02392663), where the nebulization of 3 saline solutions (HS7%, HS7%+ HA0.1% and IS0.9%) was compared in bronchiectasis stable patients. Sputum samples expectorated spontaneously were collected before and after nebulization. To measure solid?s concentration, samples were weighed in the liquid state, then frozen at -80?C and lyophilized (Telstar Lyoquest-55 Plus, Spain) for 48 hours. In addition, the colour of the sample was also classified according to the Murray scale. Results: 38 sputum samples were included: 15 IS, 13 HS and 10 HS+HA. The reduction in solid?s concentration after nebulization was greater for HS+HA compared to HS and IS (Table 1). The only solution that generated changes in sputum colour after nebulization was HS+HA, with 3 purulent samples pre-nebulization that changed to mucoid (p<0.01). The solid?s concentration and the sputum colour presented a positive and moderate correlation (r=0.566, p<0.01). Conclusions: In patients with bronchiectasis, nebulization of HS+HA seems to generate a greater decrease in the solid?s concentration and a greater change in sputum colour compared to IS and HS.