Abstract
Introduction:
The utility of TB PCR (Xpert Ultra®) in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) samples remains unclear in a low incidence high resource setting.
Aims:
To analyse the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert Ultra for the detection of MTB in BAL samples in culture positive pulmonary TB cases.
Methods:
This multicentre prospective study across 10 units analysed BAL samples from January 2021 to December 2022. Routine bronchoscopy results for TB PCR, microscopy and culture were reviewed alongside their clinical data. Turnaround times (TAT) were measured for each test.
Results:
226 BAL samples were analysed with a median age of 57.1 (IQR 42.0-69.8), M:F ratio of 134:92, 22 patients with previous TB, 42 with diabetes and 13 with HIV.
23 cases were culture positive with a median time to culture positivity of 20 days (IQR 15-3-28.5). TB PCR and smear had a median TAT of one day. There were 3/226 trace readings on Xpert Ultra, none with previous TB, and 2 of which were culture positive. All trace readings were clinically treated for TB. The diagnostic accuracy of the tests are summarised in Figure 1. 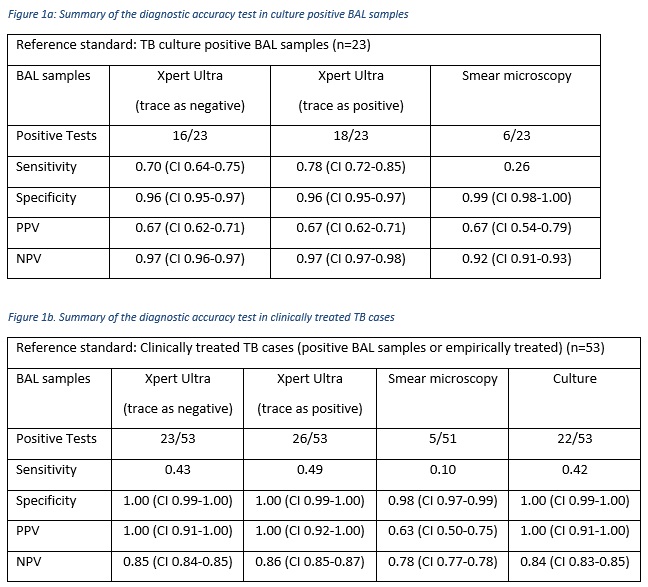
The sensitivity of Xpert Ultra in the culture negative TB treated group was 0.26 (trace as negative) and 0.29 (trace as positive).
Conclusion:
Xpert Ultra has a higher diagnostic yield compared to smear microscopy in BAL samples. It is a rapid diagnostic tool with the additional benefit of detecting rifampicin resistance.