Abstract
Purpose
The study aimed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of the BBIBP COVID-19 vaccine in terms of humoral and cellular immune response.
Methods
A multicenter study of 353 healthy adults was conducted, with participants receiving three doses of the vaccine, and their antibody levels were assessed through various methods such as cVNT, pVNT, sVNT, and CyTOF.
Results
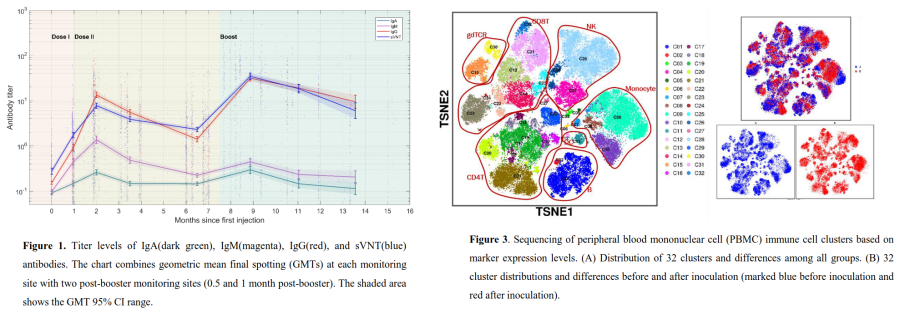
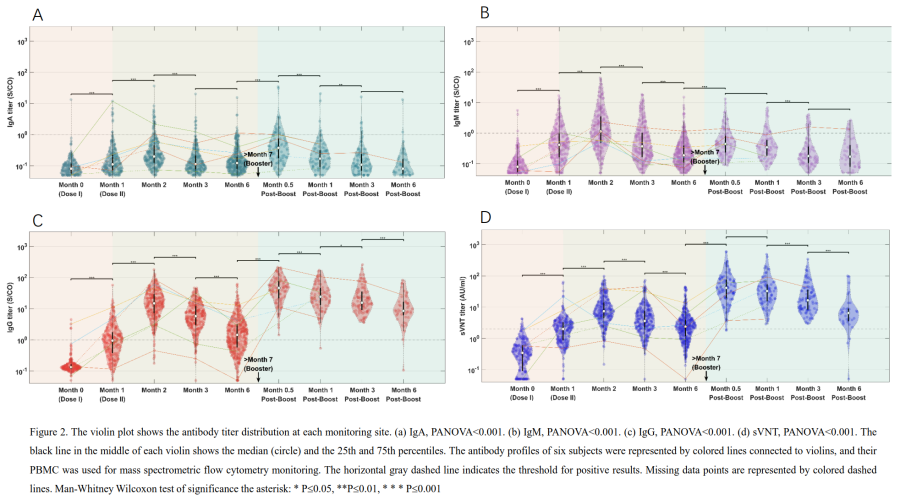
Results showed SARS-CoV-2-IgA/IgM/IgG antibodies and sVNT antibodies peaked 1 month after the 2nd vaccine dose, then declined slowly (Fig. 1). There is a significant increase in antibody levels 0.5 months after the booster, resulting in a 13.2-fold increase in neutralization titer. Despite a decline, the antibody levels remained above the positive threshold for 2 months (Fig. 2). The study found no significant differences in immunological antibody levels based on gender or age. However, B cell expression levels showed a significant decrease 3 months after the booster (Fig. 3).
Conclusion
The study provides strong evidence for the effectiveness of the BBIBP vaccine in increasing protection against COVID-19 and maintaining humoral immunity for an extended period.