Abstract
Objective Mask choice is a key parameter in adaptation of CPAP treatment. Two parameters of poor tolerance are cutaneous over pressure and unintentional leaks. The aim of this study was to create a test bench for masks to compare and localize cutaneous pressure areas, while monitoring leak flow.
Methods The test bench is made of an artificial head on which customs-made pressure sensors were placed. Artificial Heads were conceived via additive manufacturing processes. printed Sensors measured electrical capacity variations (%VC) positively correlated with cutaneous pressure. For 4 different masks, different harness tightening conditions were tested. A flowmeter was used to monitor total leaks (Fig 1).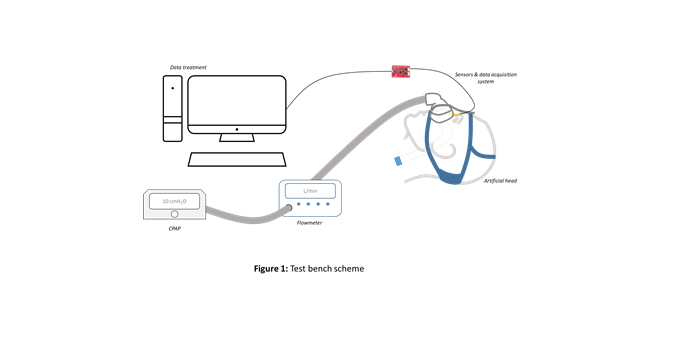
Results Sensors detected tightening conditions: average of +2 %VC when harness was tight. This increase varied according to masks [1; 3]%VC and the sensors position [1.3; 2.2]%VC (Fig 2).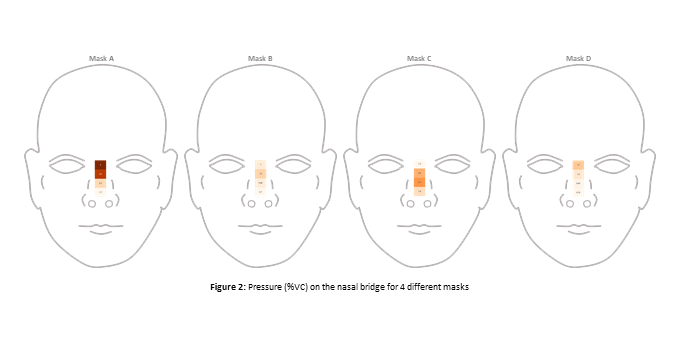
Conclusion This bench test allowed us to compare masks between them. Indeed it allowed us to localize and compare high pressure areas according to the mask. Such data could be used to help get the best mask choice for patients or develop the most adapted features.