Abstract
Introduction: Anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS) is a connective tissue disease typically associated with myositis and interstitial lung disease (ILD). Pulmonary hypertension (PH) has been described in this group but has not previously been well characterised.
Methods: Our database was searched for CTD-PAH patients from 2010-22 and data from patients with a definite/highly probable diagnosis of ASS based on existing criteria were collected from patient records and retrospectively analysed.
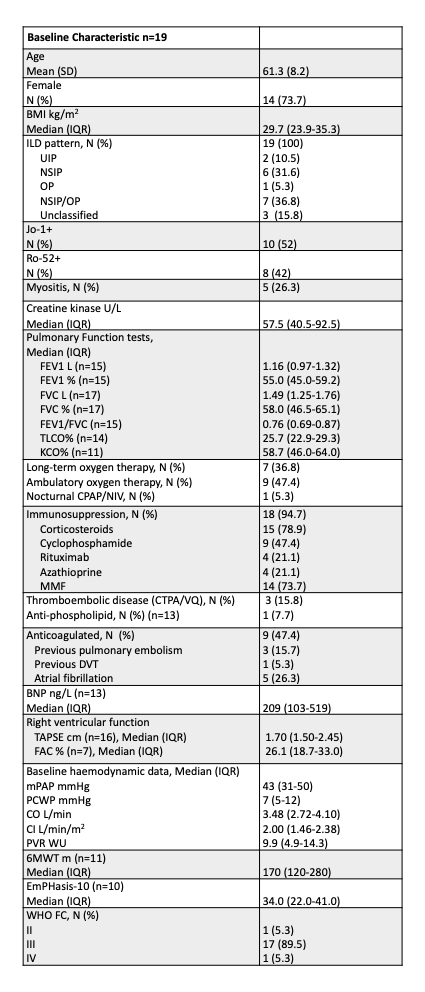
Results: Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. 13/19 (68%) were treated with monotherapy (PDE5 inhibitor) and combination therapy (PDE5 inhibitor and ERA) was initiated in the remaining 6/19 (32%). Repeat haemodynamics were obtained in 7/19 (37%) at median 32(6-57) months. There was no change in mPAP (43 to 40mmHg (IQR 33-45), p=0.6) or PVR (9.9 to 8.9WU (IQR 3.8-13.4), p=0.4). There was a trend towards reduction in BNP (209 to 107ng/L, p=0.1) and EmPHasis-10 score (34 to 26, p=0.6). 6MWT distance was unchanged (170m to 180m, p=0.3). FVC (58 to 57%, p=0.9) and TLCO (26 to 23%, p=0.3) were unchanged. Mortality was 37% (7/19), median time from diagnosis to death 16 months (IQR 9-41). However a subgroup (7/19, 37%) survived >60 months.
Conclusion: It is unclear if it is beneficial to treat ASS-PH patients as Group 1 rather than Group 3 PH. Further research may ascertain which ASS-PH patients benefit from pulmonary vasodilators.