Abstract
Introduction: The Bronchiectasis Impact Measure (BIM) is a validated tool measuring patient perceived quality of life (QoL) that shows strong correlations with the respiratory symptoms? domain of the Quality of Life - Bronchiectasis (QoL-B) questionnaire. Assessing the convergent validity of the BIM with other QoL-B domains and similar tools such as the Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire (BHQ) are required.
Methods: Patients with bronchiectasis who were participants in the multicentre EMBARC-BRIDGE study and based in the UK, completed the BIM, QoL-B and BHQ while clinically stable.
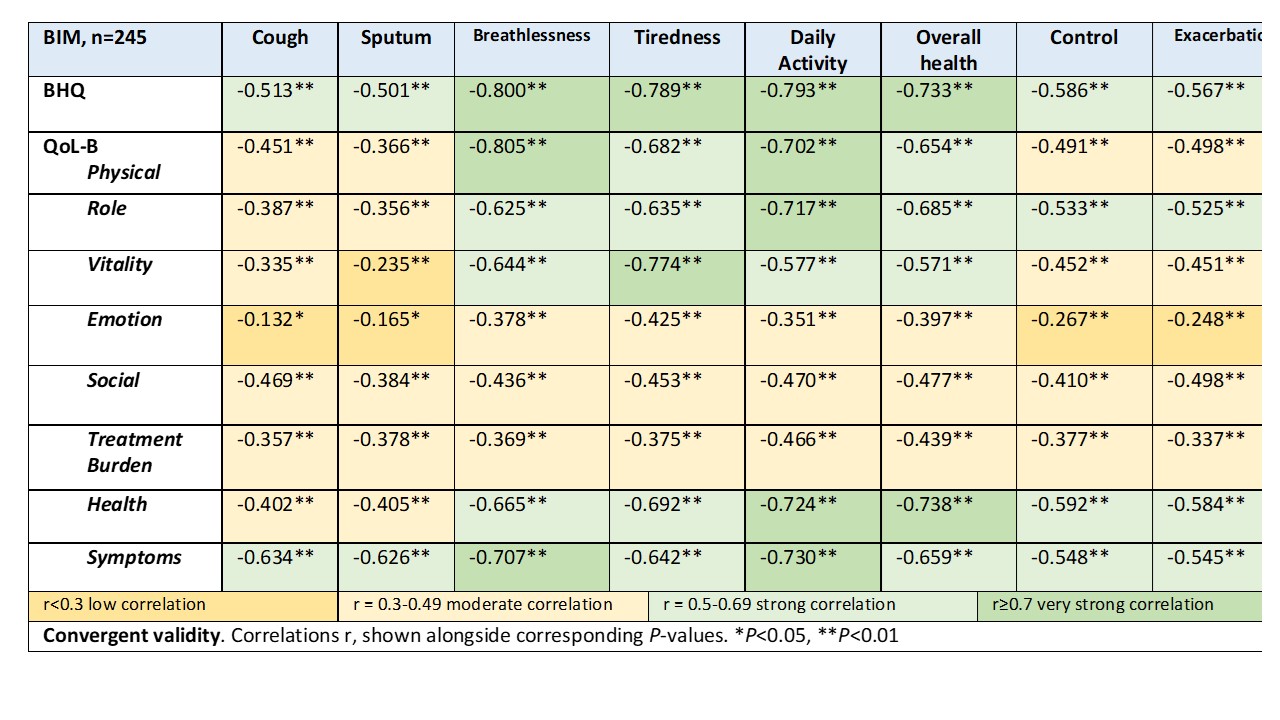
Results: 245 patients were included; 53% were female with mean age 68.5 years. 46% of participants had idiopathic bronchiectasis and disease severity was moderate (median [IQR] bronchiectasis severity index; 5 [3-7]). There were statistically significant associations between all BIM items and BHQ total score and all QoL-B domains. All BIM items had strong correlation with the BHQ (r= -0.501 [sputum] to -0.800 [breathlessness], P<0.01) and QoL-B symptoms score (r= -0.545 [exacerbation] to -0.730 [daily activity], P<0.01); however, the QoL-B Emotion domain showed the weakest correlation, ranging from r= -0.132 [cough] to -0.425 [tiredness] (Table1).
Conclusion: The BIM items are strongly associated with the BHQ and all QoL-B domains.