Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Known etiologies of airway-centered interstitial fibrosis, as hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), chronic microaspiration-induced pneumonitis (ASP) and collagen vascular disease (COL), are related to immune/inflammatory mechanisms. However, the role of dendritic cell is not known yet.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES: To determine dendritic cell profile for differential diagnosis in airway-centered interstitial fibrosis.
METHODS: 21 surgical lung biopsies with definitive diagnosis for HP, ASP and COL after MDD by ATS/ERS criteria were selected between 2017-2021. Immunohistochemical for Mannose, CD1c and Langerin with dendritic morphology cells and their morphometry were performed.
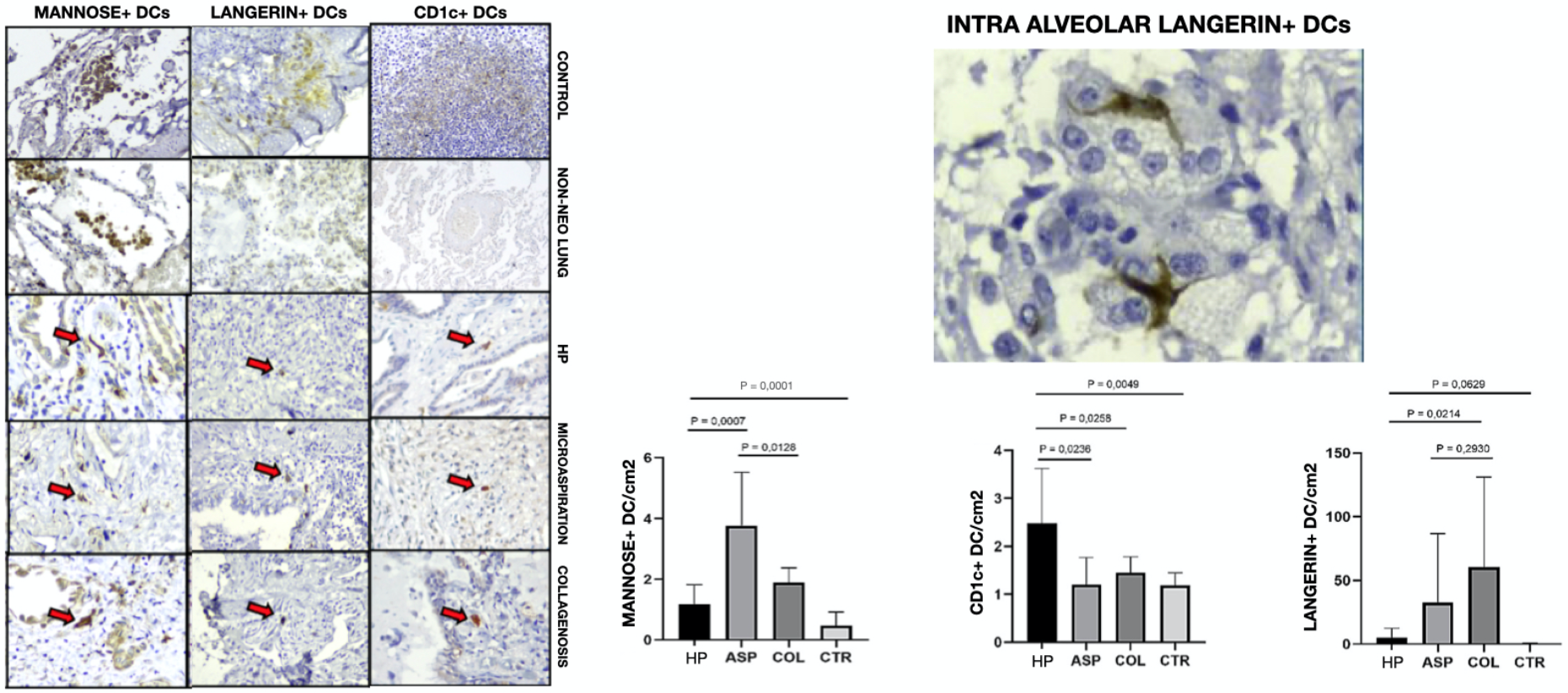
RESULTS: While Mannose+DC was higher in ASP compared to HP and COL, CD1c+DC was higher in the PH group than ASP and COL. However, Lagerin+DC was higher in COL than PH and yet showed intraluminal expression.
CONCLUSION: The increased expression of Mannose+DC in ASP, CD1c+DC in HP and Langerin+DC in COL reflects their different pathophysiological pathways in airway-centered interstitial fibrosis, which may be related to a more accurate differential diagnosis. (FAPESP No 2019/01517-3, No 2019/19591-5, 2021/10981-5 and FAEPA - No 1988/2019)