Abstract
Introduction: Stroke volume (SV) has emerged as a prognostic marker in pulmonary arterial hypertension (Humbert M et al. Eur Heart J 2023;61: 2200879). It has been reported that SV derived non-invasively from left ventricular volumes with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) shows good agreement with the gold standard method direct Fick (Mauritz GJ et al. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2008 5;10:51). Whether such agreement holds true across different degrees of tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is still unclear.
Aim: Assess the impact of tricuspid regurgitation on the accuracy of CMR-derived SV measured by left ventricular volumes compared to the gold-standard Fick method, in pulmonary hypertension patients.
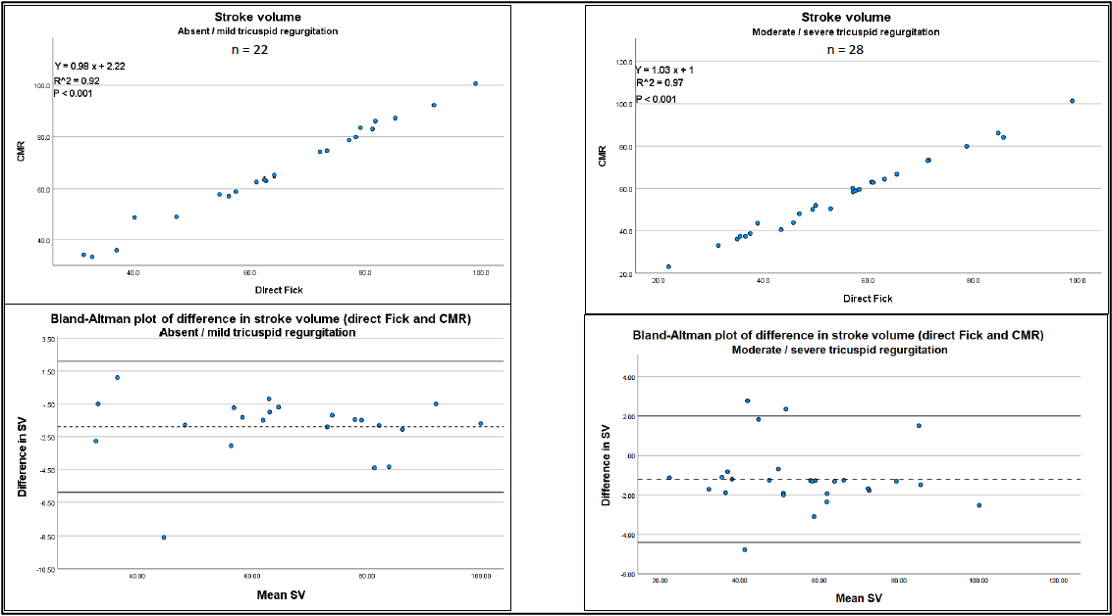
Methods: 50 PH patients (62% group 1, 20% group 4, 12% group 2, 6% group 3) underwent CMR within 24 hours from RHC between 05/2022 and 01/2023. Bland-Altman analysis was used to compare the degree of agreement between direct Fick and CMR.
Results: For SV by CMR vs direct Fick in patients without or with mild TR mean difference was -1.9 mL, with limits of agreement of -5.9 mL and 2.1 mL. For SV by CMR vs direct Fick in patients with moderate/severe TR mean difference was -1.2 mL, with limits of agreement of -4.4 mL and 2 mL.
Conclusions: SV measurements derived from left ventricular volumes on CMR agree well with direct Fick measurements irrespective of the degree of TR.