Abstract
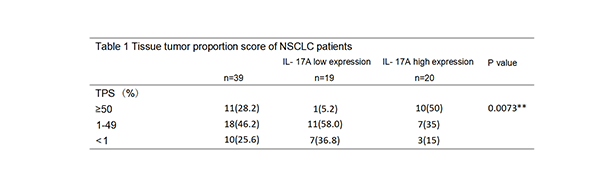
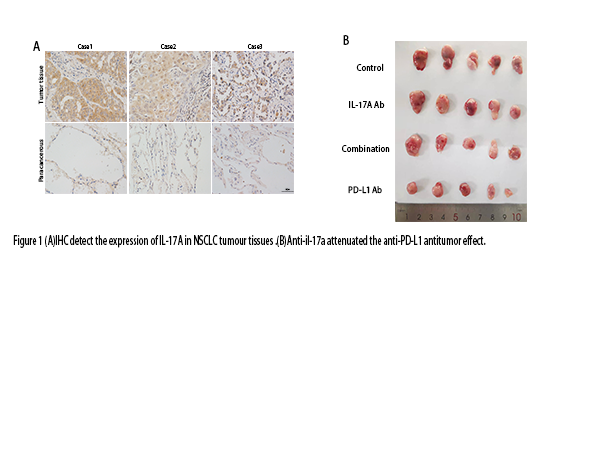
The pro-inflammatory factor IL-17A is commonly expressed in NSCLC which may lead to immunotherapy resistance.The role and mechanism of IL-17A in the development and immunotherapy of NSCLC were investigate.Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of IL-17A in the tumour tissues of 39 NSCLC patients.Data show that IL-17A was highly expressed in NSCLC tumor tissues (87.2% positive rate)and positively correlated with PD-L1 expression (r=0.6121,P<0.0001). IL-17A promoted lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT,accompanied by increased expression of PD-L1. IL-17A inhibited autophagy via the ROS/Nrf2/P62 pathway led to PD-L1 degrade less.In vivo, Anti-IL-17A activated autophagy and reduced PD-L1 expression in tumour cells. When combined with an anti-PD-L1 drugs, PD-L1 expression in tumour tissue was reduced and the therapeutic effect was decreased. IL-17A promotes NSCLC progression.Blocking of IL-17A may decrease the expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells, leading to non-response to immunotherapy or secondary drug resistance.