Abstract
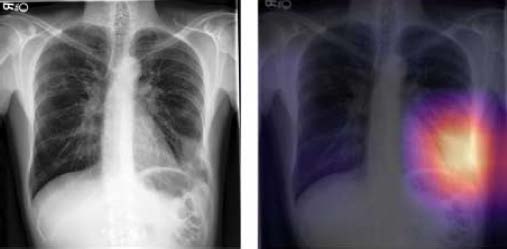
Introduction Chest imaging is needed for diagnosis and treatment of patients suspected of pneumonia. Radiologist interpretations are delayed and may not specify findings. CheXED processes digital chest Xray images using artificial intelligence (Irvin J Thoracic Imaging 2022), but needed development and validation for urgent care clinics (UCC).
Methods CheXED was trained with PA and Lateral CXR images from 9,174 patients, categorized by review of radiologist reports from 28 Utah (USA) UCCs 2019-2021. After the updated CheXED was deployed to 5 UCCs, we compared radiologist reports to CheXED for radiographic pneumonia on PA and Lateral CXRs done 21.12.22 to 5.1.23 in consecutive patients >12 years old. Two CXRs where CheXED and reports differed were resolved by image and clinical note review by a Pulmonologist (ND) to determine presence/absence of radiographic pneumonia.
Results Study population had a median age of 45 +/- 19.1 years; 15.7% were diagnosed with pneumonia by the UCC clinician. CheXED and the radiologist agreed on 38 of 40 CXRs; CheXED was judged correct once and the radiologist in the other. Kappa agreement = 0.84.
Conclusion CheXED accurately identified radiographic pneumonia in UCC patients <1 second after image uploading. CheXED embedded within ePNa electronic clinical decision support (Dean AJRCCM 2022 205:1330) is likely to improve UCC diagnosis and treatment of patients suspected of pneumonia.