Abstract
Aims
Emphysema in COPD can lead to loss of microscopic pulmonary arteries and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Aim: To determine the association between pulmonary artery volume on CT and mortality.
Methods
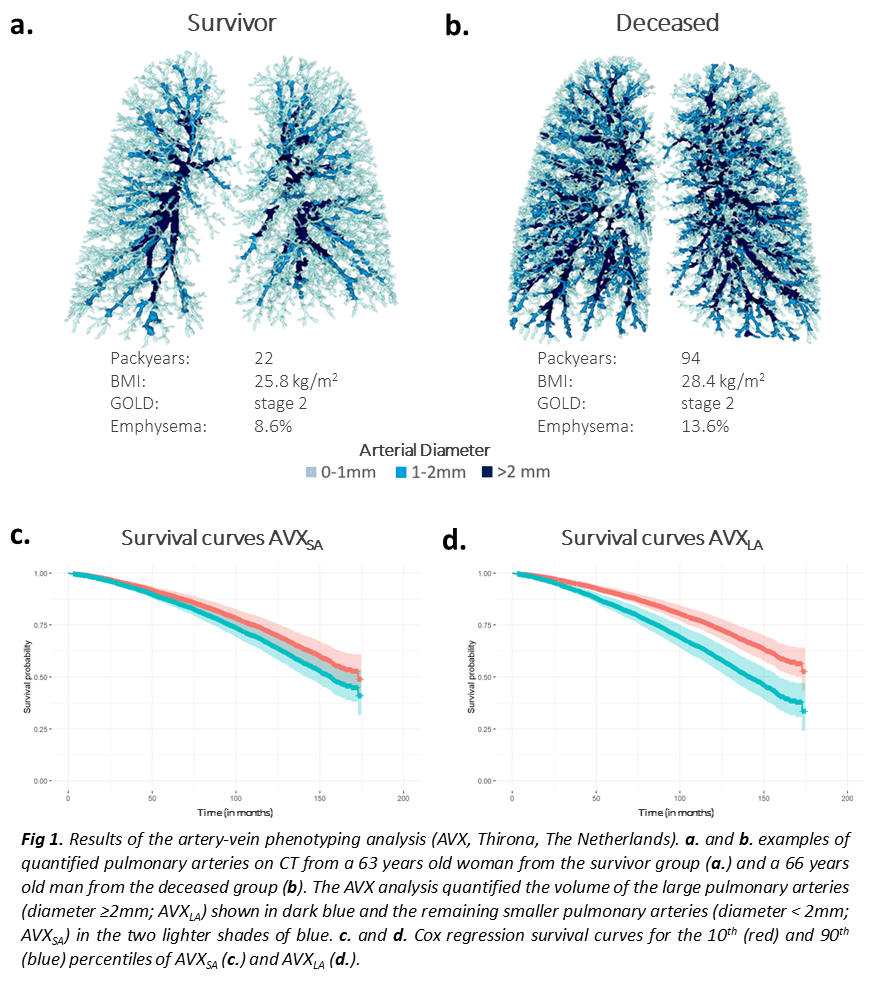
The artery-vein phenotyping analysis (AVX) was performed using the AI-based lung quantification platform LungQ (Thirona, The Netherlands). AVX quantified total volume of small (diameter <2mm; AVXSA) and large (?2mm; AVXLA) pulmonary arteries from inspiratory CT in 7903 participants in the COPDGene study, normalized for body height. Cox regression analysis was used to analyze associations between AVX scores and mortality. Corrections were made for age, sex, BMI, FEV1%predicted, mMRC, 6MWT, smoking status, emphysema, airway wall thickness, coronary artery calcium score, severe exacerbations, and scanner model.
Results
Average age was 60.1±9.0 years, 3594 (45.5%) subjects had COPD. AVXSA was 103.3±21.5 mm3/cm and AVXLA was 201.9±68.1 mm3/cm. Higher AVXSA and AVXLA were both associated with higher mortality, HR 1.23 (CI 1.10-1.38) and HR 1.17 (CI 1.12-1.22) per 50 mm3/cm increase, respectively.
Conclusions
An increased pulmonary arterial volume is associated with mortality, independent of emphysema. AVXSA and AVXLA may be markers of secondary blood flow redistribution and arterial dilatation due to destruction of more distal arterioles, potentially leading to pulmonary hypertension.