Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
A variety of systems are routinely used to measure respiratory parameters during CPET. The accuracy of most systems remains unexplored or has been assessed only by comparing systems against each other. We use a metabolic simulator to investigate the accuracy of fifteen popular CPET systems for assessing respiratory gasses during metabolic exercise testing.
METHODS:
A metabolic simulator (Relitech Systems, NL) was used to simulate breath-by-breath gas exchange at known volumes. V?O2 and V?CO2 range 0.75 - 4.2 L/min, at breath frequency between 10 - 80 /min and V?E up to 160 L/min. RER simulated between 0.75 and 1.05.
The performance of 15 different CPET devices from 10 manufacturers was investigated: Cosmed (Quark, K5), Cortex (MetaLyzer, MetaMax 3B), Vyaire (Vyntus CPX, Oxycon Pro), Maastricht Instruments (Omnical), MGC (Ergocard Clinical, Ergocard Pro, Ultima), Ganshorn/Schiller (PowerCube Ergo), Geratherm (Ergostik), VO2master (VO2masterPro), PNO? (PNO?), and Calibre Biometrics (Calibre).
RESULTS:
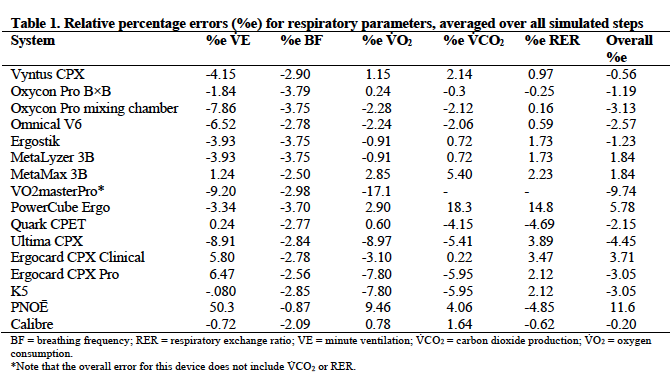
Absolute percentage errors ranged from 0.08-50.3% for V?E, 0.24-17.1% for V?O2, 0.30-18.3% for V?CO2, and 0.16-14.8% for RER.
CONCLUSION:
The error of measured respiratory parameters between CPET systems is generally <5% but differs substantially between systems.
We recommend verification with a metabolic simulator to become a routine part of yearly quality check of CPET equipment.