Abstract
OBJECTIVE ARISE (NCT04677543) aimed to support validation of PRO instruments, including QOL-B RD in patients with MACLD. Correlation between culture conversion and respiratory symptoms measured by QOL-B RD was also examined.
METHODS Adults with newly diagnosed or recurrent non-cavitary MACLD were randomized 1:1 to amikacin liposome inhalation suspension (ALIS arm) 590mg or ELC (comparator arm), plus AZI [250mg] and ETH [15mg/kg] once daily for 6M, followed by 1M off-treatment. The association of culture conversion by M6 and M7 with change from baseline to M7 in QOL-B RD was assessed.
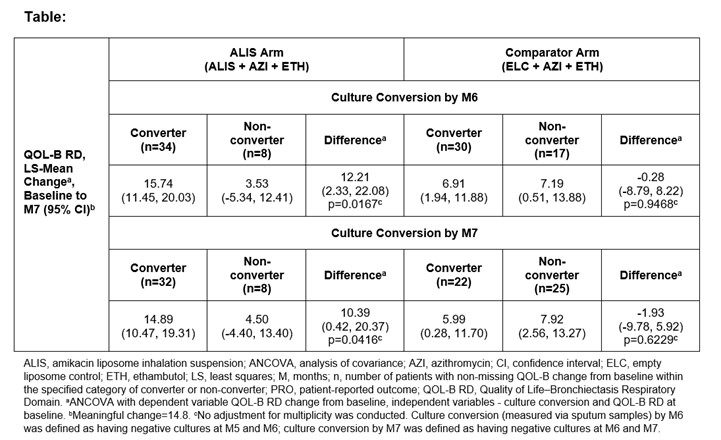
RESULTS Rates of culture conversion by M6 and M7 were higher in the ALIS (N=48) vs comparator (N=51) arm (80.6% vs 63.9%; 78.8% vs 47.1%). A positive correlation was observed between change in QOL-B RD at M7 and converters by M6 or M7 in the ALIS arm (point-biserial correlation coefficients: 0.36 and 0.35). ALIS converters had greater improvement in QOL-B RD vs non-converters (Table). No correlation between change in QOL-B RD at M7 and culture conversion by M6 or M7 was seen in the comparator arm.
CONCLUSION The larger change in respiratory score and higher rate of culture conversion are reflected in the significant, positive correlation observed in ALIS-treated patients with MACLD. A 15M confirmatory study is ongoing (ENCORE; NCT04677569).