Abstract
Background: Bronchiectasis is a suppurative lung disease which might benefit from dipeptidylpeptidase-1inhibitor treatment.
Objective: To evaluate the effects of HSK31858 in Chinese adults with bronchiectasis.
Methods: This was a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Bronchiectasis patients with ?2 annual exacerbations received placebo, 20mg HSK31858, or 40mg HSK31858 (1:1:1) for 24 weeks. The primary end point was the exacerbation frequency.
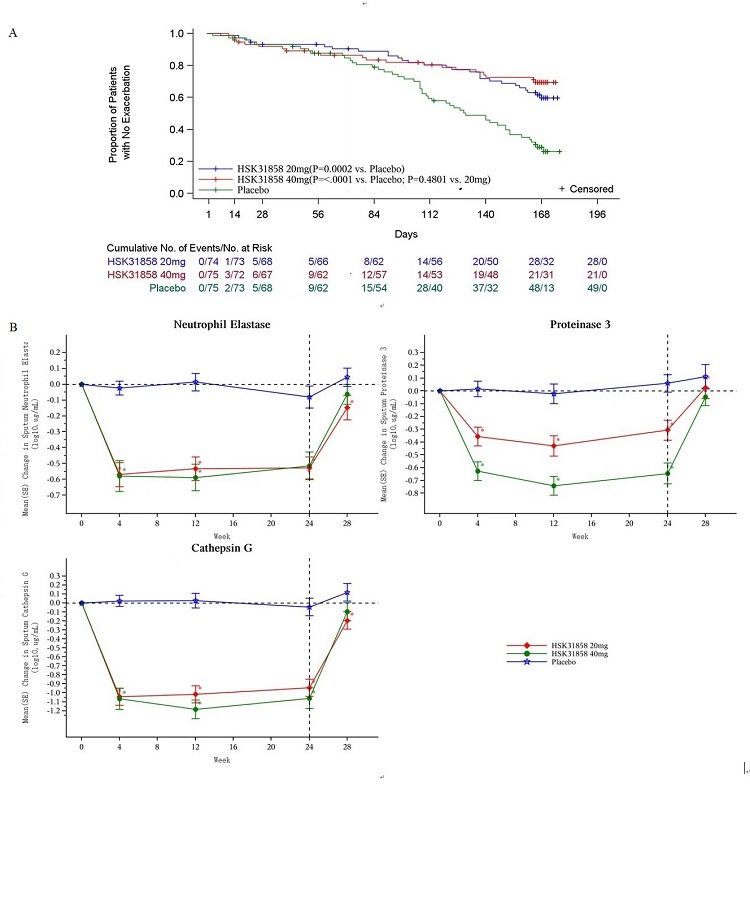
Results: Overall, 75 patients were allocated to placebo group, 75 to 20mg HSK31858 group, and 76 to 40mg HSK31858 group. Both 20 mg (HR=0.52, 95%CI: 0.34-0.79) and 40 mg HSK31858 (HR=0.40, 95%CI: 0.25-0.64) markedly reduced exacebation frequency compared with placebo. Both HSK31858 20mg (147.2 days vs. 124.1 days, P=0.0038) and 40mg (146.2 days vs. 124.1 days, P=0.0089) yielded notably longer mean duration to the first exacerbation. 20mg HSK31858 significantly reduced sputum purulence score compared with placebo (P=0.0007). The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events in HSK31858 20mg (86.5% vs. 85.3%, P>0.05) and 40mg groups (88.0% vs. 85.3%, P>0.05) was comparable with that in placebo group.
Conclusion: HSK31858 is safe and effective for ameliorating neutrophilic inflammation in bronchiectasis.
Figure 1. Time to the first exacerbation (A) and sputum NSPs activity (B)